Why the Latest News on Tariffs Makes Contract Manufacturing in India More Attractive Than in China
- Mandeep Singh, CEO

Does your business currently do contract manufacturing in China? Do the tariffs cause you to consider relocating operations to India?
Read on for the latest updates on the tariff situation and to find out if India’s rising competitiveness can take on China’s dominance.
Breaking Tariff News for China, India, U.S.
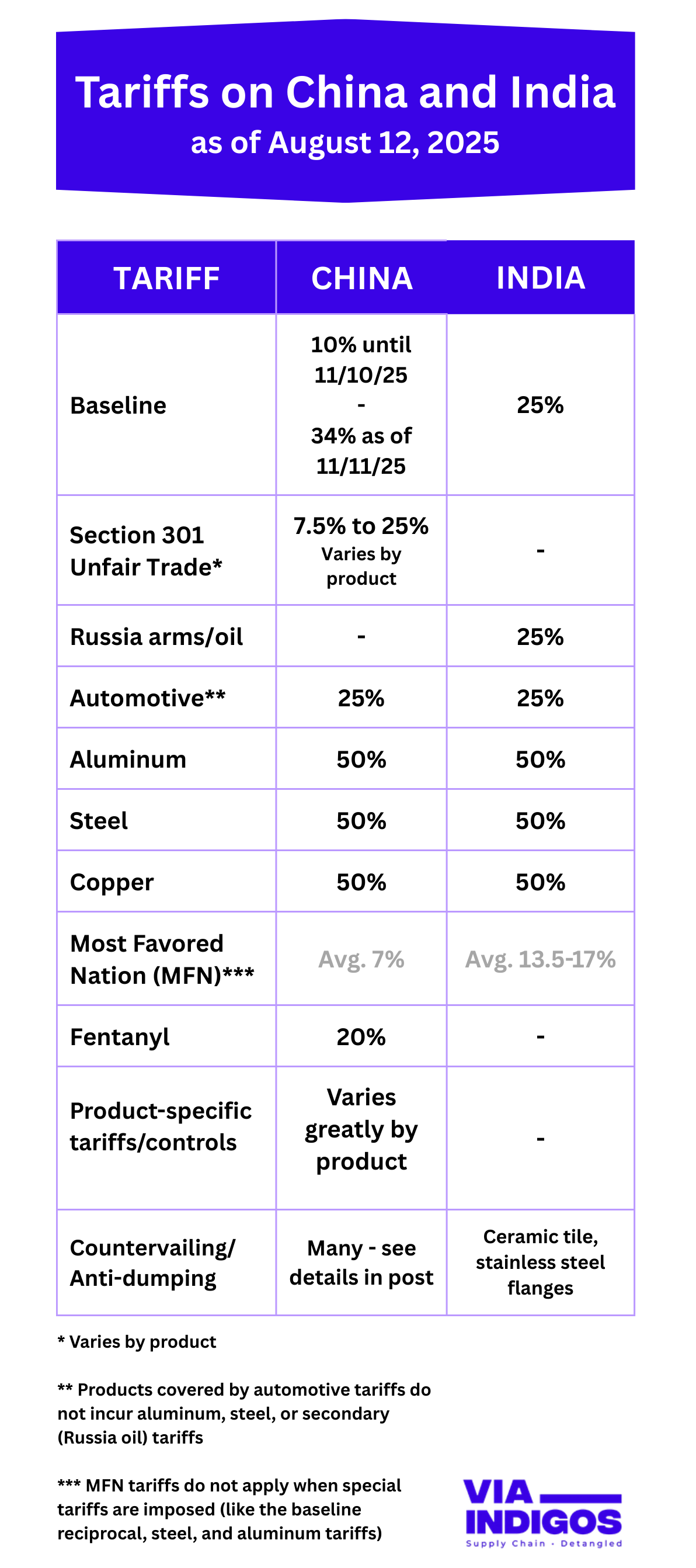
Permission granted to republish the image above with attribution and a link to this content.
IMPORTANT: Tariffs are continually changing and importers should not rely on this information to determine their actual tariff obligations.
Importers get the official costs of tariffs imposed primarily through customs authorities of the importing country, which calculate tariffs based on the Harmonized System (HS) codes of the products being imported.
Aug. 27, 2025 is the date the secondary (Russia oil) tariff is scheduled to take effect on India unless negotiates to lower it are successful.
Aug. 12, 2025 the 34% baseline tariff on China was scheduled to go back into effect; however, it was deferred until Aug. 12 and then deferred on Aug. 12 for another 90 days until Nov. 10, 2025.
If no agreement is reached, the baseline will go up to 34% on Nov. 11, 2025 barring any additional changes.
Aug 6, 2025 Trump announced a 25% secondary tariff for buying Russia oil. It does not stack with automotive tariffs. This 25% will be imposed on or after 12:01am Eastern on August 27th, 2025 unless another deal is negotiated.
July 30, 2025 Trump imposed a 25% tariff rate on India and “50% tariffs on semi-finished copper products starting Aug. 1, but he stopped short of applying the duties to copper scrap and input materials”.
July 7, 2025 Official White House announcement Extending the Modification of the Reciprocal Tariff Rates. This changed the end of the 90 day extension from July 9, 2025 to August 1, 2025.
Additional information from Christine Zhang and Tony Romm can be seen in this NY Times article on Trump’s New Tariff Threats.
July 6, 2025 Trading Economics reported when “President Donald Trump announced Sunday that any country aligning with the “anti-American policies” of the BRICS bloc will face an additional 10% tariff.“
July 2, 2025 Vietnam tariff deal at 20%. Chinese transshipments subject to 40% tariffs. Full known details here.
June 11, 2025: President Trump announced a deal has been made with China.
They have agreed to return to the framework previously agreed to in Geneva. Trump said that China will provide rare earth minerals and magnets “up front”.
The U.S. will impose 55% tariffs on China and China’s tariffs on the U.S. will be 10%. Additionally, Chinese students will be permitted to continue in U.S. universities.
However, the agreement still awaits final approval from both President Trump and President Xi.
May 30, 2025: Speaking to U.S. Steel workers, President Trump announced:
"We’re going to bring it from 25% to 50%, the tariffs on steel into the United States of America."
President Trump Tweet
The change would affect steel and aluminum and go into effect June 4, 2025. It affects not just raw steel and aluminum, but also derivitive products.
Steel Industry News analyzed the impact.
May 28, 2025: A U.S. trade court ruled that the 1977 International Economic Powers Act does not permit the president to impose tariffs the way Trump did.
May 29, 2025: One day later, a federal appeals court temporarily reinstated Trump’s tariffs.
While appeals are considered, the tariffs remain in effect.
The U.S. Court of Appeals for the Federal Circuit has ordered plaintiffs to respond by June 5 and the government to respond by June 9.
As of May 15, 2025, China is continuing to block export of rare earth minerals in spite of agreeing to permit the export under the Geneva trade statement.
May 12, 2025 U.S. tariffs were dropped for 90 days from 145% to 30%. The tariffs the Chinese levied dropped from 125% to 10%.
The 90 day reciprocal tariff pause is set to expire Aug. 12, 2025.
India and the U.S. plan to have a mutually beneficial interim agreement prior to the July 8 pause expiration.
China also agreed to at least temporily remove the restrictions on export of rare earths and to stop blacklisting certain U.S. companies.
April 26, 2025 News breaks that China has quietly exempted a growing list of “critical U.S. goods” from their 125% tariffs.
Latest on the Proposed and Later Paused U.S. Tariffs
The exact amounts of tariffs on any particular product is a complex calculation that is changing daily.
On Saturday, April 12, 2025, CNN reported there will be no tariffs on electronics including smartphones, computers, and chips.
But the electronics tariff relief could be temporary.
It is critical to understand the difference between existing tariffs, reciprocal tariffs, and sector-specific duties.
"While Trump has put a 90-day pause on reciprocal tariffs, the abatement doesn't apply to sector-specific duties."
Brian Sozzi, Executive Editor, Yahoo!Finance Tweet
There is good news for manufacturers shipping goods. There is clarification about the “savings clause” that exempts goods already on the water from reciprocal tariffs.
But elsewhere Thompson Hine indicates that this does not apply to China!
International Trade practice group Thompson Hine explains:
"Articles the product of any country that were (1) loaded onto a vessel at the port of loading and in transit on the final mode of transport prior to entry into the United States before 12:01 a.m. EDT on April 5, 2025 (i.e., the 10% tariff), AND (2) are entered for consumption, or withdrawn from warehouse for consumption, on or after 12:01 a.m. EDT on April 5, 2025, and before 12:01 a.m. EDT on May 27, 2025, are not subject to the additional 10% duty rate."
Thompson Hine SmarTrade
China Retaliated; Trump Further Increased Their Tariffs
This trade war started long before tariffs. AP News reported that the U.S. limited exports of advanced semiconductors to more companies December 2, 2024.
China responded December 3, 2024 by restricting exports of rare earth minerals including antimony, gallium, germanium, and others.
On April 4, 2025, China restricted export of rare earth magnets and six additional rare earth minerals.
CNBC reports that China responded by increasing their 84% tariff on U.S. goods to 125% and would ignore any further U.S. increases.
With both sides refusing to back down, until they agree to negotiate, manufacturing in China will be far more costly.
According to NBC News, the current total tariffs on China were “54% and possibly higher” before the new increase to 125%.
President Trump responded to China’s retaliatory reciprocal tariffs by increasing the tariff on China to 125%.
Then, on Thursday April 10, 2025, the White House clarified that the 125% was in addition to the tariffs Trump had already added for a total tariff on China of 145%.
145% Tariffs are a Minumum!
The 145% is a minimum as there are additional sector-specific tariffs on steel, aluminum, cars and other goods.
But that isn’t all. Toy manufacturers were shocked to be hit with 170% tariffs due to Section 301 tariffs being stacked on the 145%!
We know this due to a viral post Courtney Peebles, Founder and Toy Designer at award winning Solobo Toys created on LinkedIn.
They do have options, though. They could move toy manufacturing to India which already has the capabilities.
On April 15, 2025, the White House published a fact sheet explaining that the 245% tariff does not apply to all imports.
"China faces up to a 245% tariff on imports to the United States as a result of its retaliatory actions. This includes a 125% reciprocal tariff, a 20% tariff to address the fentanyl crisis, and Section 301 tariffs on specific goods, between 7.5% and 100%."
The White House Tweet
And Don't Forget Duties on Top of Tariffs!
On top of the tariffs, duties may also apply. For example:
- Anti-dumping (AD) duties: Vary widely, sometimes 10%–100%+ depending on the case.
- Countervailing (CVD) duties: Also variable, sometimes 5%–50%+.
- Other fees: Harbor maintenance, merchandise processing, etc.
So, the total duty rate could be:
- Section 301 rate (e.g., 145% or 170%)
- PLUS the regular duty rate (often 2.5%–8%)
- PLUS any AD/CVD duties if applicable
Tariffs on India, Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam
Meanwhile, according to Reuters, India’s tariffs were set to increase to 26% or 27% before the pause.
But they may not stay that high as India and the U.S. were already in talks:
"India is the only country with which the US is deeply engaged in trade negotiations. Among all trading partners, it is only India to which the US has sent a delegation of trade negotiators."
Mukesh Jagota, Financial Express
Before the pause, The Financial Express believed India was the winner of the tariff war:
"India is positioned favorably in the US tariff war with lower duties than competitors like China and Vietnam. Ongoing BTA negotiations with the US offer potential for further tariff reduction on Indian exports."
Mukesh Jagota, Financial Express
In contrast, Trump’s proposed tariffs on other countries’ manufacturers are most likely to consider moving product to were:
- Malaysia 24% – July 7, 2025, Trump notified Malaysia that their tariff will be 25% starting August 1, 2025.
- Thailand 19% announced Aug 4, 2025 Previously confirmed to go to 36% effective August 1, 2025. However: “Deputy Prime Minister and Finance Minister Pichai Chunhavajira expressed confidence that Thailand can negotiate a US tariff deal below 36% before the August 1 deadline, stating the government has contingency plans ready if negotiations fail.”
- Vietnam 20% – lowered to 20% announced July 2, 2025; Chinese transshipments tariff set to 40%. Full known details here.
All tariffs are subject to change based on the results of negotiations.
Trump has announced a 90 day pause on over 75 countries who did not retaliate and have requested negotiations:
"Trump said he was authorising a universal "lowered reciprocal tariff of 10%" as negotiations continued."
Emma Rossiter & Sam Hancock, BBC News
India rejected any idea of retaliatory tariffs in favor of a bilateral trade deal:
"India is among the countries that have adopted a cautious approach in reacting to potentially seismic action, saying it is engaged with the Trump administration on the bilateral trade agreement (BTA)."
Jayanth Jacob, The New Indian Express
We know from Reuters that Malaysia, Thailand, and Vietnam do not plan to retaliate and have requested to negotiate so the pause should apply to them as well as to India.
However, some older tariffs are likely to stay in place, at least for now. When definitive information is available related to the countries mentioned here, we will update this content.
Can India Compete with China for Contract Manufacturing?
While there are challenges related to moving to India, find out how VIA INDIGOS has overcome all of them.
For decades, China has been the world’s sole contract manufacturing superpower, solidifying its status as the “world’s factory.”
It has achieved this through a combination of strategic policies, opening investment doors, a skilled workforce, and robust infrastructure.
But the World Bank ‘India Development Update’ of September 2024 concluded:
"As China withdraws from low-skill manufacturing due to increasing wages, India has the potential to capitalize on this opportunity."
WorldBank Tweet
Both China and India have utilized public private partnerships (PPPs) and successfully extended production lines into new sectors.
And in the 2025 Behind Asia video, ‘Can India Replace China as the World’s Manufacturing Hub’ [below], they argue that China’s declining and aging population will result in:
- A reduced labor force
- Higher wages
- More costly social services, pensions, and healthcare
VIDEO: Can India Replace China in Manufacturing?
Play this video for why many believe India will eventually be able to replace China manufacturing.
[Click in the center – the play button is hard to see because the thumbnail image is also red.]Although China is currently much stronger, they note that many manufacturers are seriously considering moving production, with India emerging as a leading alternative.
India has a major advantage with their average salaries as of 2023 coming in at 82.84% less than China’s:
- India: $2,900 USD annually
- China: $16,900 USD annually
India is rapidly becoming a significant player in global manufacturing for key sectors, particularly in contract manufacturing.
This is thanks to government reforms, a young and cost-effective workforce, and the increasing need for companies to diversify their supply chains.
As global manufacturing shifts gears, businesses face a critical choice: stick with China’s established dominance or explore India’s rising competitiveness.
The stakes have never been higher. In this detailed analysis, we’ll explore:
- China’s manufacturing dominance
- Factors driving India’s rise
- The challenges each country faces
You will discover what this means for businesses navigating today’s rapidly evolving supply chain landscape.

The Rise of China’s Manufacturing Dominance
China’s position as global manufacturing industry leaders has been built on years of strategic investments and policy initiatives.
However, according to the World Bank Group:
"In China, growth is expected to decline from 4.9% in 2024 to 4.1% in 2026."
World Bank Global Economic Prospects January, 2025 Tweet
The 2025 worldwide manufacturing statistics from World Population Review show China leading with 31.63% and a value of $4,975,614.

Here are the key factors contributing to its dominance:
Unparalleled Economies of Scale
China has built an industrial ecosystem that supports mass production.
Industries ranging from electronics to textiles benefit from a deeply integrated supply chain network where raw materials, components, and finished goods flow seamlessly.
- For example, the Pearl River Delta is a hub for electronics manufacturing, with companies like Foxconn producing devices for global giants like Apple.
- Also, the Pearl River Delta is a hub for electronics manufacturing, with companies like Foxconn producing devices for global giants like Apple.
- The Yangtze River Delta, on the other hand, is known for its advanced materials and automotive manufacturing.

In NPR’s India is hoping its manufacturing sector will profit from Trump’s tariffs on China, they confirm India’s market share:
"Now India manufactures nearly 15% of all Apple iPhones, and is the second largest exporter after China. India hopes to nearly double its share of iPhone manufacturing to 25% in the coming years. Last year it exported over $20 billion worth of mobile phones — a 44% rise over 2023, spotlighting how rapidly this market is growing."
Diaa Hadid, NPR
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)#2 have been pivotal in China’s economic transformation, with Shenzhen’s SEZ standing out as a prime example. Established in 1980, Shenzhen’s SEZ was among the first four in China, designed to attract foreign investment through incentives like tax breaks, streamlined regulations, and enhanced infrastructure.
The impact of these SEZs is evident in several key statistics:
- Foreign Direct Investment (FDI): By 2007, Shenzhen’s SEZ had attracted substantial foreign investment, contributing significantly to its rapid industrialization and economic growth.
- Economic Growth: In 2016, Shenzhen’s GDP growth rate was 9.0%, surpassing the national average and highlighting the SEZ’s role in fostering economic development.
- But this is expected to drop to only 5.5% in 2025. While helping drive investment, growth is slowing.
- Industrial Output: The added value of Shenzhen’s high-tech industry reached 656.002 billion yuan in 2016, reflecting a 12.2% year-on-year increase and underscoring the SEZ’s success in promoting advanced industries.
- This has also declined to 8.8% as of 2023.
These figures underscore the effectiveness of SEZs like Shenzhen in attracting foreign investment and driving economic growth through favorable policies and infrastructure development.
Advanced Infrastructure
China has invested trillions of dollars in infrastructure over the past three decades:
- Over 150,000 miles of highways and a robust high-speed rail network facilitate efficient logistics.
- Ports like Shanghai and Ningbo-Zhoushan are among the busiest in the world, ensuring the smooth export of goods.

China’s Advanced Infrastructure
Technological Edge
China has moved beyond low-cost manufacturing to dominate in high-tech industries:
- Semiconductors: China remains the global leader in semiconductor equipment spending, projected to invest $38 billion in 2025 despite a 24% YoY decline.
- Green Technology: The country is a leader in producing solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicle batteries. They control over 75% of the electric vehicle battery market.

Semiconductor
Government Policies
China’s government has actively supported industrial growth through subsidies, low-interest loans, and investment in education to create a skilled workforce.
Global Supply Chain Integration
Over the years, China has embedded itself in the global supply chain. For instance:
- Electronics: Companies worldwide rely on Chinese manufacturers for components.
- Textiles: From fast fashion to high-end apparel, China produces a significant portion of global garments.

Navigating China’s Dominance in the Global Semiconductor Market
While China has long been the backbone of global manufacturing, the need for diversification is more pressing than ever.
Shifting trade policies, rising tariffs, and geopolitical uncertainties are driving businesses to explore alternatives.
This is where India enters the conversation—not as a replacement but as a promising partner in building resilient supply chains.
India’s Manufacturing Ascent: A New Challenger
India has traditionally been seen as a services-driven economy, with IT and software development taking the spotlight.
However, the manufacturing sector is undergoing a transformation. Key factors driving India’s competitiveness include:
Make in India Initiative
Launched in 2014, the Make in India initiative aims to position India as a global manufacturing hub.
The India program focuses on improving the ease of doing business, reducing regulatory barriers, and attracting foreign direct investment (FDI).
For example, Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in renewable energy opened to 100% FDI, attracting $3.8 billion in solar sector investments over three years.
An important aspect of the Make in India campaign is the value of the collaborative model of India’s global partners.
These various knowledge partners close gaps in innovation, technology transfer, and workforce upskilling.
This is especially beneficial in certain sectors such as defense manufacturing.

Shift to India to reduce tariffs.
Special Economic Zones (SEZs)
Established under the Special Economic Zones Act, 2005, these zones aim to enhance infrastructure, create jobs, and promote technology transfer.
As of 2023, India has 272 operational SEZs, employing 2.8 million people and generating $133 billion in exports (60% from services, 40% from goods).
Notable zones include:
- Kandla SEZ (Gujarat): Largest goods exporter ($38 billion in FY 2022-23).
- SEEPZ (Maharashtra): Focused on electronics and gems/jewellery ($149.6 billion exports in 2020-21).
- Noida SEZ (Uttar Pradesh): Multi-product exports ($65.5 billion in 2020-21).
India’s infrastructure projects (industrial corridors, smart cities) aim to connect multiple enterprises into clusters, mirroring China’s success in creating enterprise ecosystems around transportation hubs and special economic zones.
Production Linked Incentives (PLI)
The Indian government has introduced PLI schemes to boost domestic manufacturing in sectors such as:
- Electronics and semiconductors.
- Pharmaceuticals and active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs).
- Automotive components, including electric vehicles.
These schemes offer financial incentives to companies that achieve specific production targets.
On March 28, 2025, the Union Cabinet approved the electronics component manufacturing scheme:
"The scheme envisages to attract investment of Rs 59,350 crore, result in production of Rs 4,56,500 crore and generate additional direct employment of 91,600 people and many indirect jobs as well during its tenure.
The Shillong Times
"This scheme aims to develop a robust component ecosystem by attracting large investments in electronics component manufacturing ecosystem, increasing domestic value addition (DVA) by developing capacity and capabilities, and integrating Indian companies with global value chains (GVCs)."
The Shillong Times

What are Production Linked Incentive (PLI) schemes?
Labor Advantage
India’s labor costs are significantly lower than China’s, with wages in India being 20-30% cheaper.
Additionally, India has a young workforce, with over 65% of the population under the age of 35, providing a sustainable labor pool for decades.

Geopolitical Shifts
The China Plus One strategy—adopted by many global companies—seeks to reduce manufacturing alternatives to China.
India, as the world’s largest democracy and a growing economy, has become a favored option.
Improving Infrastructure

What is the Sagarmala Initiative?
Although historically a weak point, India is making significant strides in infrastructure:
- The Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor (DMIC) is a mega-project aimed at creating industrial hubs with world-class logistics.
- Ports modernization projects such as the Sagarmala Programme are improving India’s maritime logistics.
- New Kerala deepwater port capable of receiving the largest “Mother” container ships. (See details here.)
- An alternative is to use fast boats to China out of the ports of Chennai, Ennore, and Kattupali.
"Its important to note that the ports of Chennai, Ennore, and Kattupali can accept the smaller vessels that are supporting fast-boat services out of China. Matson's fast-boat service is all sub 4000T vessels as an example. The biggest knock on South East India has consistently been the inability for larger mother vessels to call directly, but for a smaller vessel fast-boat service that would not be an issue."
Connor Helm, Ocean Procurement Manager, Flexport
Tech-Driven Growth
India is embracing Industry 4.0, with advancements in IoT, automation, and AI:
- The country is rapidly expanding its capabilities in smart manufacturing.
- Innovation hubs and tech parks are driving research and development in areas like aerospace, defense, and medical devices.
In ULL’s A decade of Make in India initiative, they note the visible momentum of a 2.6x growth in the renewable energy sector as the most striking indicator the India initiatives are working.
Key Comparisons: India vs. China in Contract Manufacturing
| Factor | China | India |
| Cost of Labor | Higher due to rising wages. | Significantly lower and more sustainable. |
| Infrastructure | World-class, highly developed. | Improvising but still inconsistent |
| Government Support | Long-standing support through subsidies. | Aggressive new reforms like PLIs and incentives |
| Technology Integration | Advanced, with a focus on robotics and AI. | Emerging, with a focus on industry 4.0. |
| Supply Chain Networks | Well-integrated and efficient. | Developing, with room for better integration. |
| Geopolitical Stability | Increasing risks due to trade tensions. | Stable and business-friendly environment. |

Challenges India Faces
While India’s rise is promising, several challenges must be addressed:
Infrastructure Bottlenecks
- Poor road connectivity and power shortages in certain areas hinder efficient manufacturing.
- Ports and logistics still lag behind global standards, but are being addressed by the Sagarmala India initiative.

Skilled Workforce
- While labor is abundant, India needs more training programs to upskill workers for high-tech manufacturing jobs.
Fragmented Supply Chains
- Unlike China, India’s supply chains are not as seamless or integrated, creating inefficiencies.
Regulatory Complexity
- Despite reforms, bureaucratic hurdles remain a deterrent for some investors.

Navigating Bureaucratic Challenges in Supply Chain Compliance
While these challenges exist, experienced partners like VIA INDIGOS ensure seamless navigation through India’s manufacturing landscape.
With on-ground expertise, we help businesses overcome these obstacles and unlock India’s potential as a global manufacturing powerhouse.
Opportunities for Businesses
1. Diversified Supply Chains
- Businesses can reduce risks by splitting operations between China and India.
2. Industry-Specific Advantages
- For labor-intensive sectors like textiles and assembly, India offers clear cost benefits.
- For high-tech and capital-intensive industries, China remains the preferred choice.
3. Long-Term Partnerships
- Companies investing in India should consider forming joint ventures with local firms to navigate regulatory complexities and leverage local expertise.

The Future of Manufacturing: Coexistence or Competition?
The global manufacturing landscape is not a zero-sum game. While India is rising, China is unlikely to lose its dominance overnight. Instead, the future may see:
- China: Retaining leadership in advanced manufacturing, robotics, and green technology.
- India: Becoming a major player in cost-sensitive and labor-intensive sectors.
The two countries could complement each other in a dual-sourcing strategy, where businesses leverage the strengths of both markets.
Why Use VIA INDIGOS to Move Manufacturing to India?
At VIA INDIGOS, we specialize in simplifying the complexities of global contract manufacturing transitions.
Whether you’re looking to reduce tariffs, diversify your supply chain, or tap into India’s growing potential, we provide end-to-end support.
With a vast network of production partners, on-ground expertise, and a commitment to quality, we handle every step of the process—from procurement to delivery.
Partner with us to build a resilient and cost-effective supply chain tailored to your business needs.

Put India's Transformational Power to Work for You
The competition between China’s powerful economy and India’s faster growth rates marks a pivotal moment for global supply chains.
For businesses, the decision to invest in one country or the other—or both—will depend on their specific needs, industries, and intellectual property risk tolerance.
India’s GDP grew by 105% in last 10 years, China at 76%, says IMF:
India’s momentum signals the dawn of a new manufacturing era, but it must address key challenges to fully capitalize on its potential.
Meanwhile, China’s technological advancements and infrastructure investments ensure its continued relevance in global manufacturing.
As the dynamics evolve, both nations will play crucial roles in shaping the future of global manufacturing.
For businesses navigating this transition, the key lies in diversification, strategic partnerships, and a long-term vision for supply chain resilience.
Mandeep Singh, CEO

With boots on the ground and a vast network of production partners, we help you cut tariffs, reduce lead times and avoid supply chain disruptions.
Let’s get started today!

-
- Posted by Mandeep Singh, CEO

-
- Posted by VIA INDIGOS

-
- Posted by VIA INDIGOS

-
- Posted by VIA INDIGOS

-
- Posted by VIA INDIGOS
July 7, 2025 Official White House announcement Extending the Modification of the Reciprocal Tariff Rates.
Additional information from Christine Zhang and Tony Romm can be seen in this NY Times article on Trump’s New Tariff Threats.
July 2, 2025 Vietnam tariff deal at 20%. Chinese transshipments subject to 40% tariffs. Full known details here.
June 11, 2025: President Trump announced a deal has been made with China.
They have agreed to return to the framework previously agreed to in Geneva. Trump said that China will provide rare earth minerals and magnets “up front”.
The U.S. will impose 55% tariffs on China and China’s tariffs on the U.S. will be 10%. Additionally, Chinese students will be permitted to continue in U.S. universities.
However, the agreement still awaits final approval from both President Trump and President Xi.
May 30, 2025: Speaking to U.S. Steel workers, President Trump announced:
July 7, 2025 Official White House announcement Extending the Modification of the Reciprocal Tariff Rates.
Additional information from Christine Zhang and Tony Romm can be seen in this NY Times article on Trump’s New Tariff Threats.
July 2, 2025 Vietnam tariff deal at 20%. Chinese transshipments subject to 40% tariffs. Full known details here.
June 11, 2025: President Trump announced a deal has been made with China.
They have agreed to return to the framework previously agreed to in Geneva. Trump said that China will provide rare earth minerals and magnets “up front”.
The U.S. will impose 55% tariffs on China and China’s tariffs on the U.S. will be 10%. Additionally, Chinese students will be permitted to continue in U.S. universities.
However, the agreement still awaits final approval from both President Trump and President Xi.
May 30, 2025: Speaking to U.S. Steel workers, President Trump announced:







